We Automate the Period-End Close for Head Offices🫰
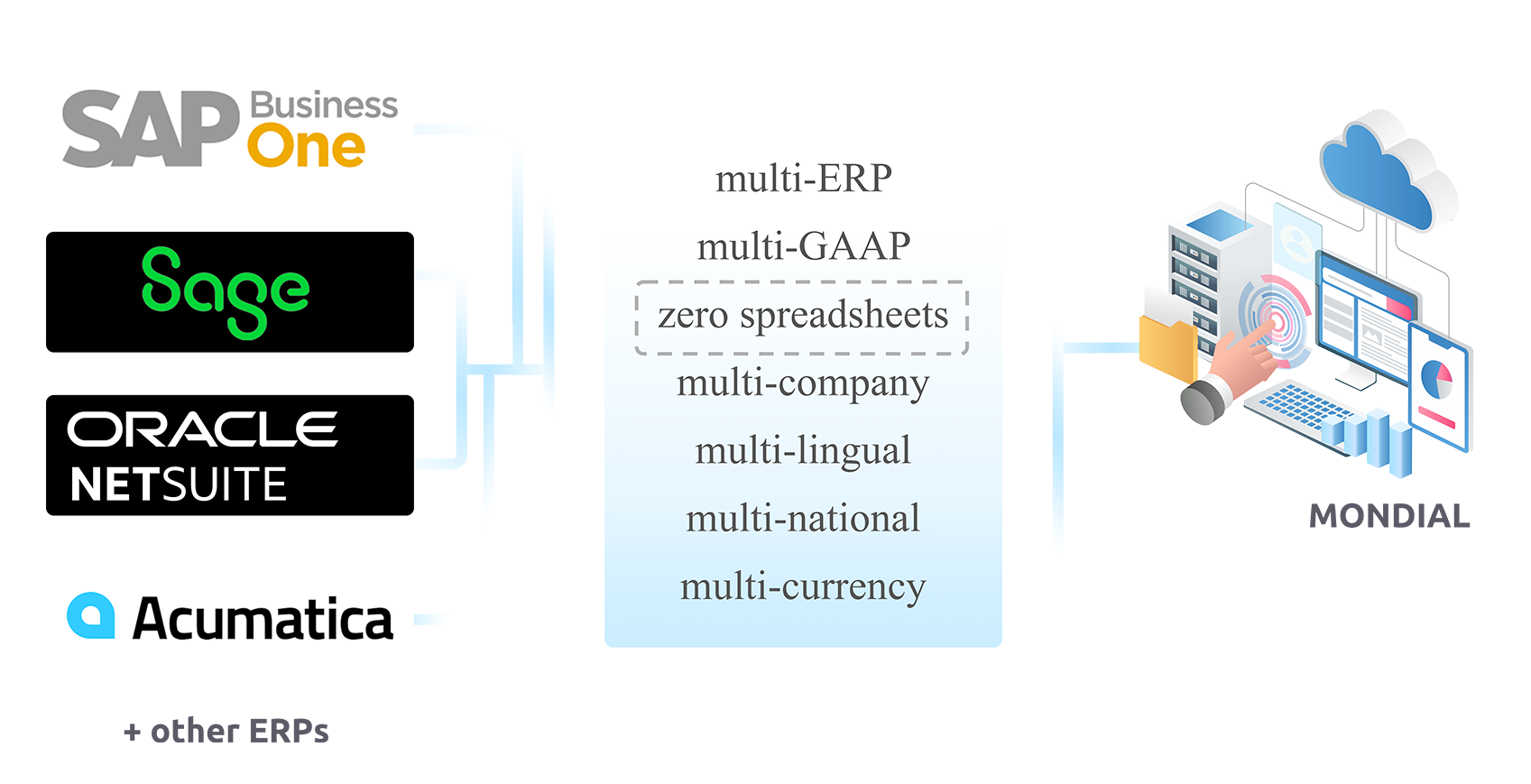
Say goodbye to ERP system incompatibilities. Mondial effortlessly consolidates operations across different ERP systems and versions, giving you a clear, unified view of your entire group.
Centralize Multi-Currency Reporting 💱💲
No more currency conversion headaches. Mondial enables centralized, group-currency reporting when local operations use local currencies, providing you with accurate, compliant, financial statements.

Harmonize Diverse Accounting Setups☄️
Forget the struggle of aligning different charts of accounts. Mondial seamlessly consolidates groups using varied account structures, ensuring consistency and clarity in your financial reporting.
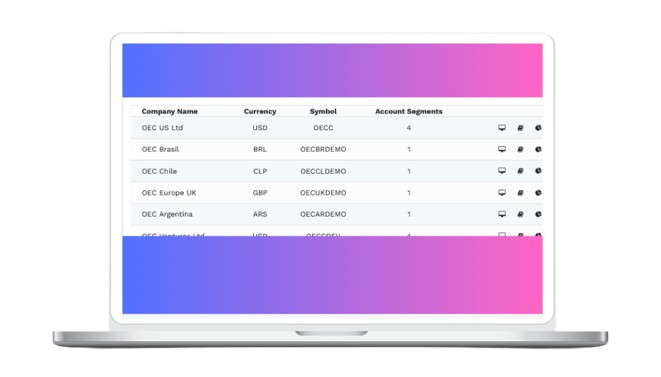
Align Mismatched Company Year-Ends 📚
Mondial helps bridge the gap for groups with companies operating different year-end dates, facilitating smoother central consolidation while supporting the on-going local reporting requirements of international or newly acquired subsidiaries.
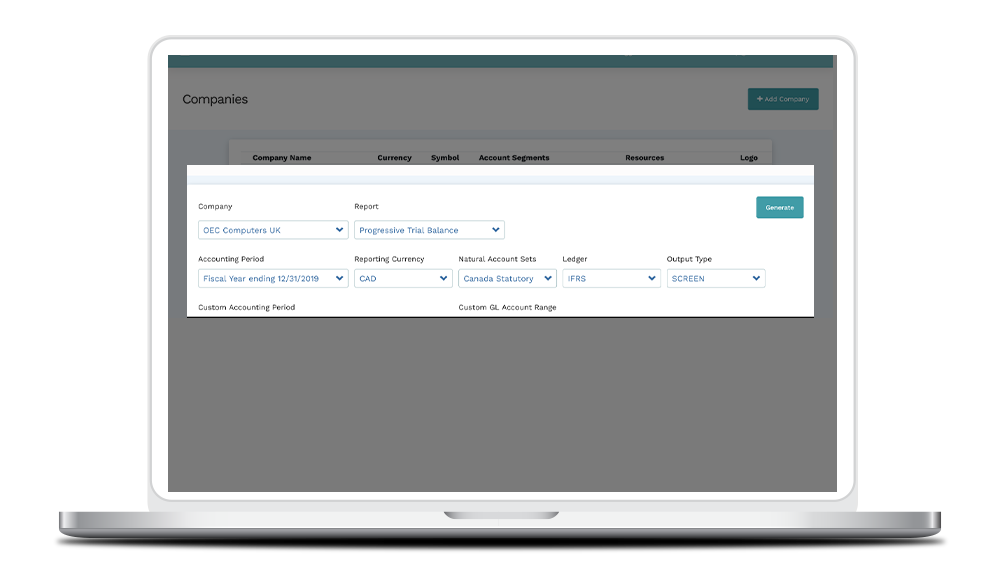
Simplify Intercompany Eliminations 🔎
Mondial helps streamline consolidations where group companies trade with each other, providing support for easy posting of the required intercompany elimination journal entries or elimination of dedicated intercompany trading accounts.
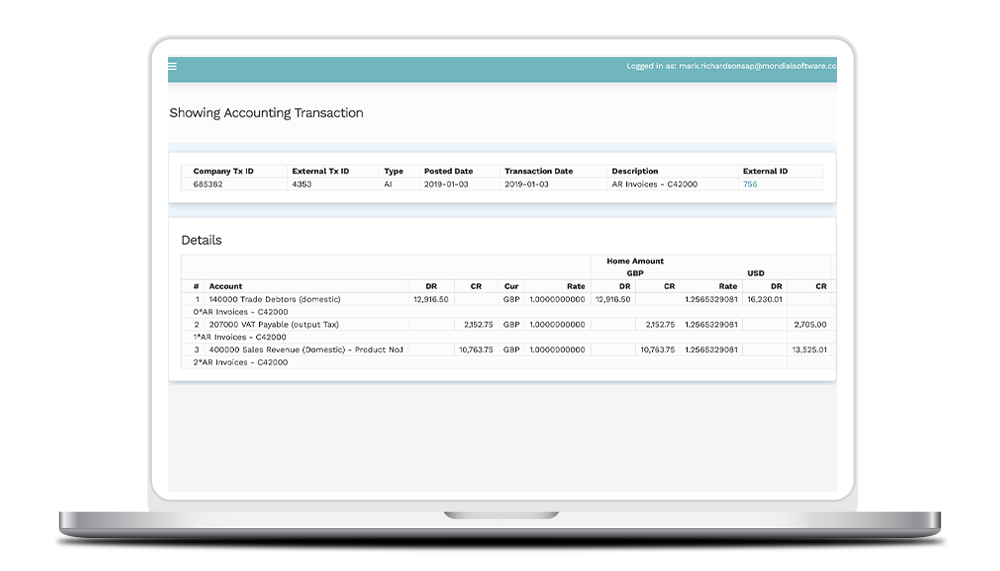
Master Multi-Standard Reporting🎉
Effortlessly switch between local GAAP and IFRS compliant views. Mondial empowers individual companies to report using multiple global accounting standards, ensuring you're always compliant and prepared for any regulatory requirement.
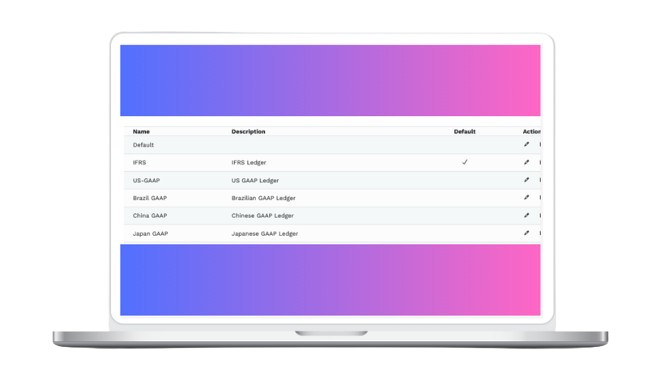
Streamline Statutory Reporting🧿
Create reports using statutory charts of accounts with ease. Mondial allows you to simply flip between your operating chart of accounts and your statutory one, providing a completely mapped audit trail, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
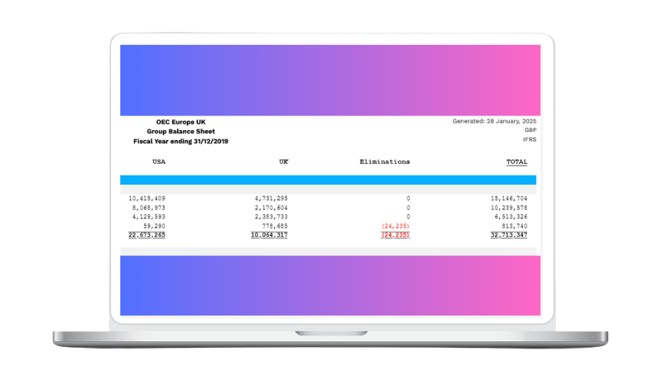
Consolidate Diverse Calendar Structures 🎨
Different operating calendar structures are no longer a barrier. Mondial can provide consolidated reporting even when group companies use accounting periods of different lengths, with different period-end dates.
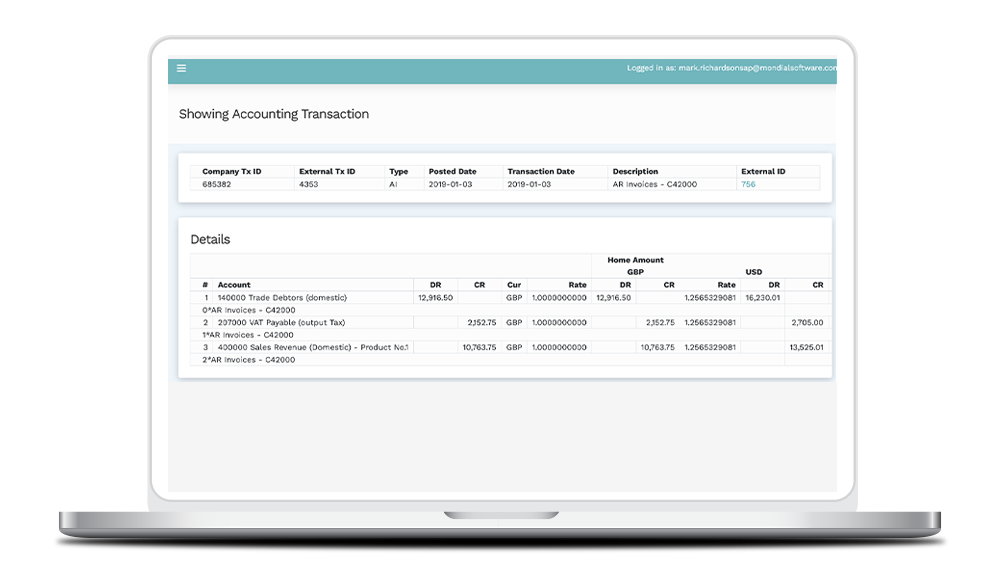
Ensure Data Sovereignty 🎲
Keep your accounting data where it belongs. Mondial supports the local storage of accounting data on in-country servers, for each company within a global operation, addressing local data sovereignty concerns and removing the risk of penalties.
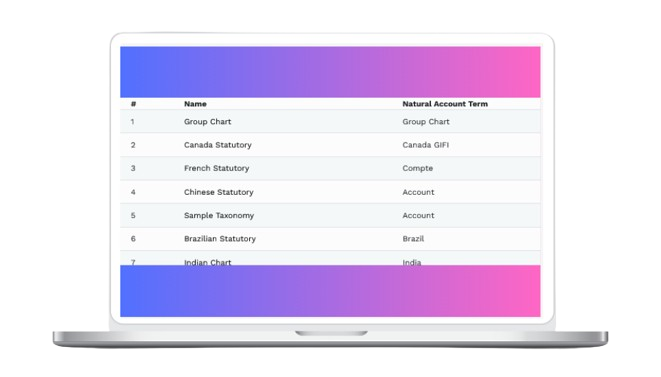
Integrate Existing Excel Templates 📊
No need to reinvent the wheel. Mondial offers integration capabilities with your existing Excel report templates, providing common data controls, preserving familiar workflows, while protecting the significant investment you’ve made in spreadsheets.
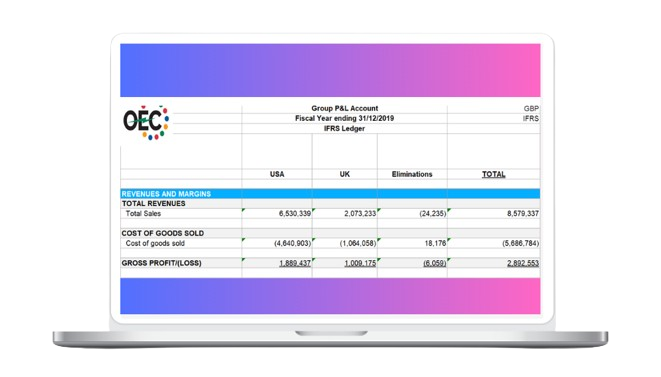
Multi-jurisdictional reporting compliance for businesses worldwide. ✒️
We combine compliance expertise with advanced ERP integration and self-service capabilities, reducing regulatory risks for customers.

Automated and Consolidated Financial Reporting for Individual and Multi-Group Companies
Empowering seamless global financial consolidation and reporting across diverse ERP systems, currencies, accounting standards, and organizational structures





Consolidate, harmonize, and streamline financial operations- disparate charts of accounts, multi- GAAP, multi-company, multiple currencies, languages and month-ends across diverse international business environments.
- Mondial intuitively understands fiscal periods, charts of account structures, transaction details and various types of balances.
- Mondial simplifies processes by recognizing concepts such as current and year-to-date amounts, debit versus credit balances, and amounts in different currencies.
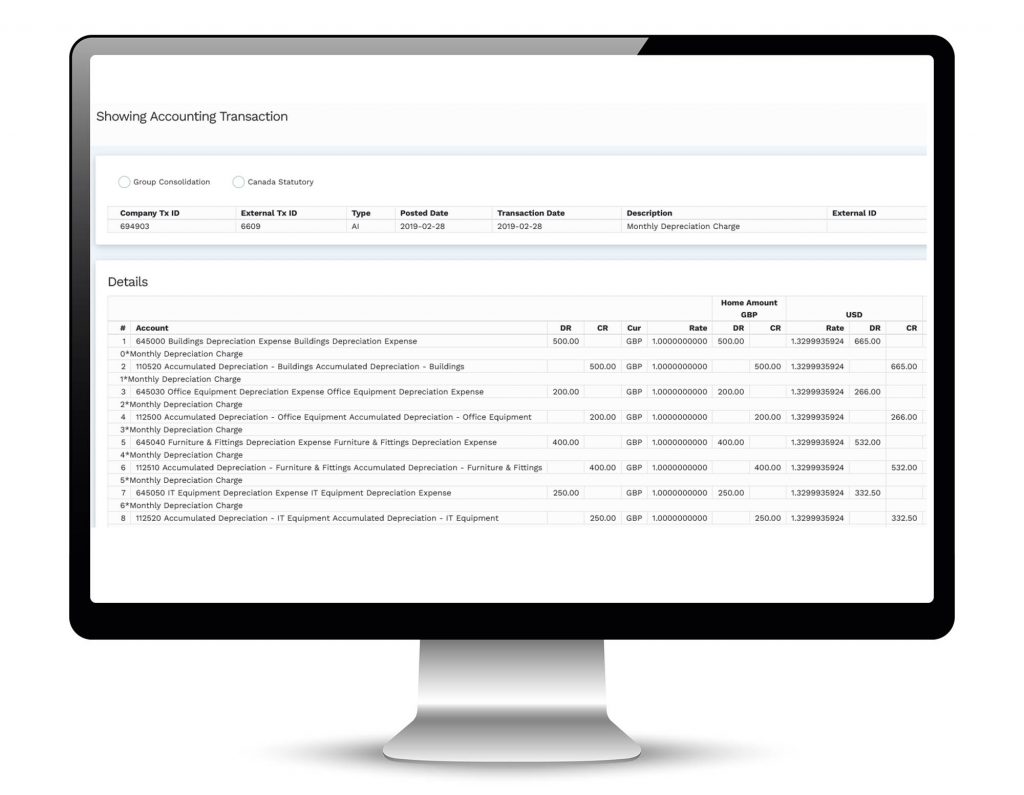
- Mondial stores every GL, AP and AR transaction from each source company to ensure that every report is based on complete and accurate information.
- Users gain additional confidence because it is easy to identify missing or duplicate accounts.
- Every transaction from the underlying system is appended with and stored in whatever currency the user needs, from whatever source the currency rate is required.
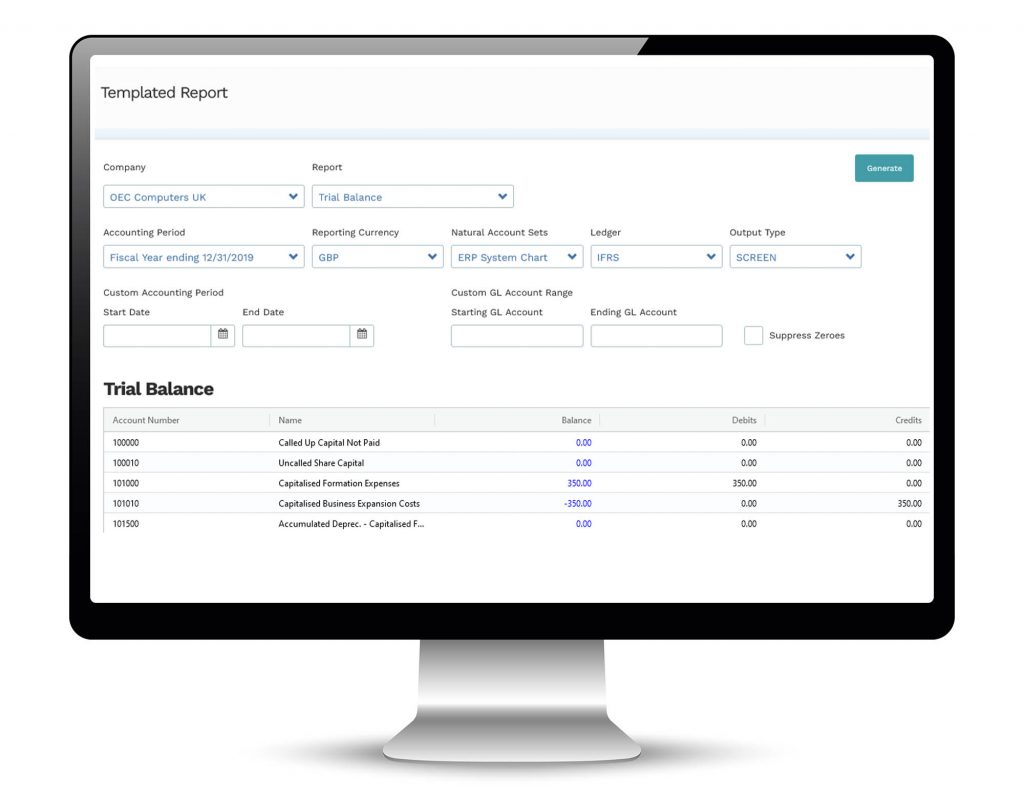
- A historically accurate trial balance can be produced in any currency and accessed on screen, printed or downloaded.
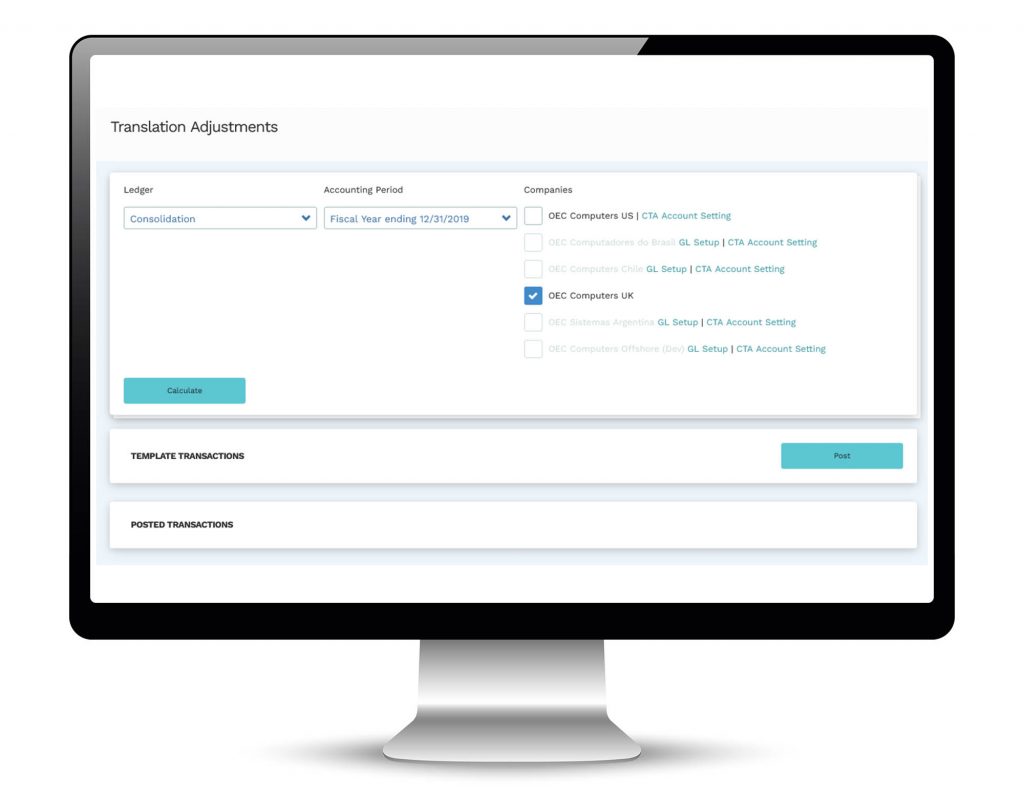
- Both soft (reporting) and hard (posting) revaluations can be performed at period end to ensure compliance with GAAP and IFRS requirements.
- Financial statements from TB’s, to P&L’s and Balance Sheets can be displayed pre or post revaluation as required.
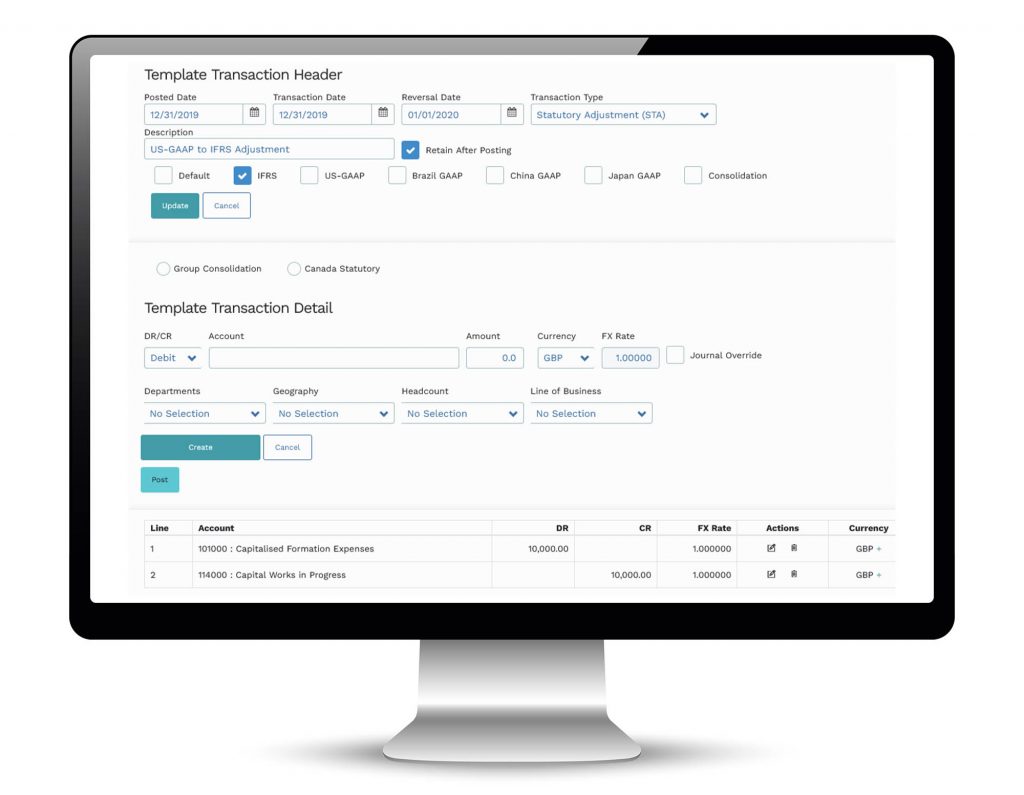
- Transactions that are sometimes difficult to enter in the accounting system such as statutory reallocations or inter-company eliminations can be entered in Mondial without impacting underlying data.
- Unique numbering sequence for all source and Mondial entered transactions provides a full audit trail across every company.
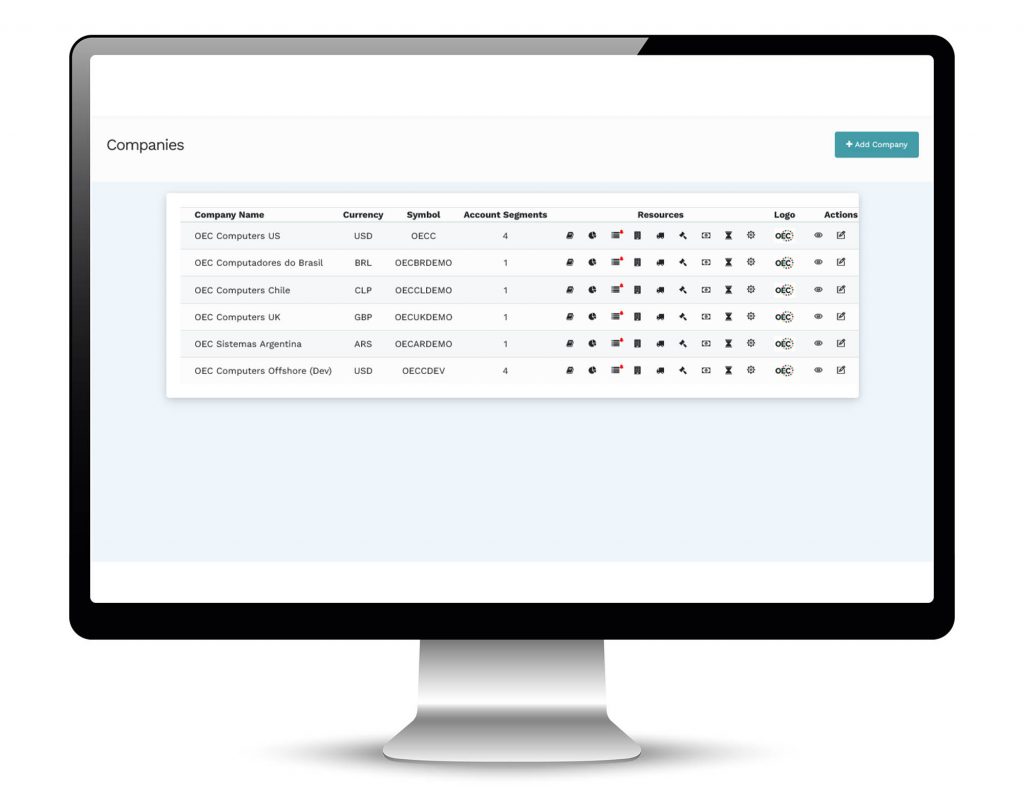
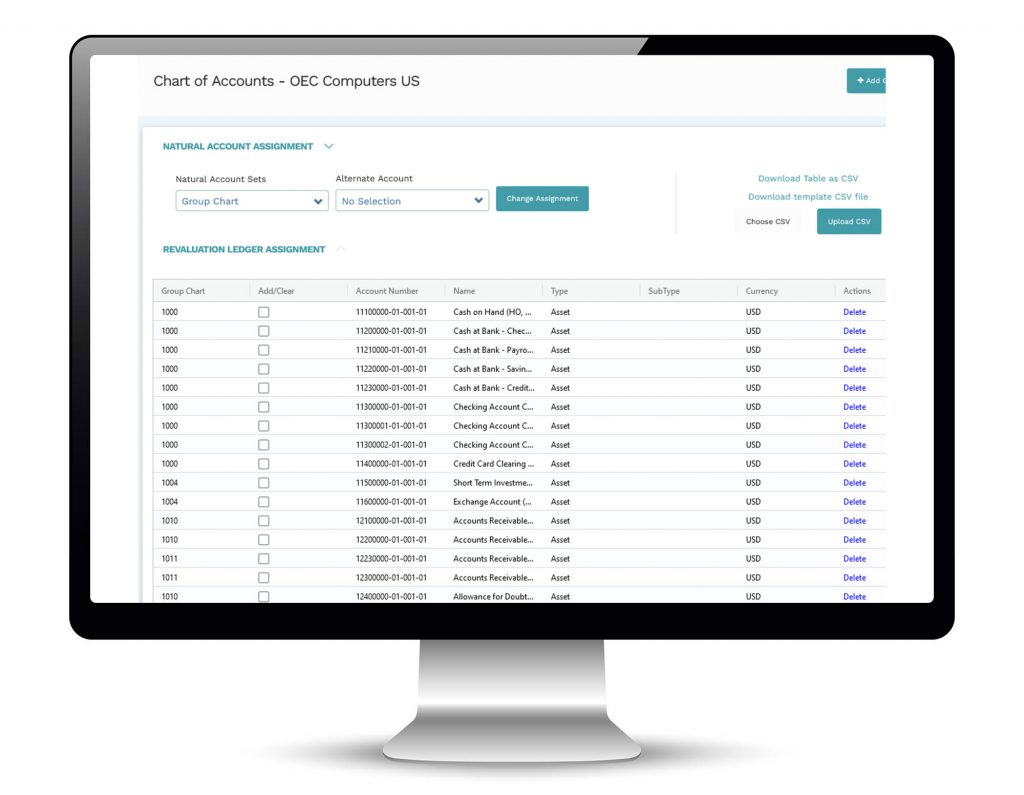
- An unlimited number of charts of account can be created in Mondial with direct account-to -account mapping from the existing chart of accounts in each source company
- This allows corporate-wide or statutory-required charts of accounts to be used for reporting with out impacting source data
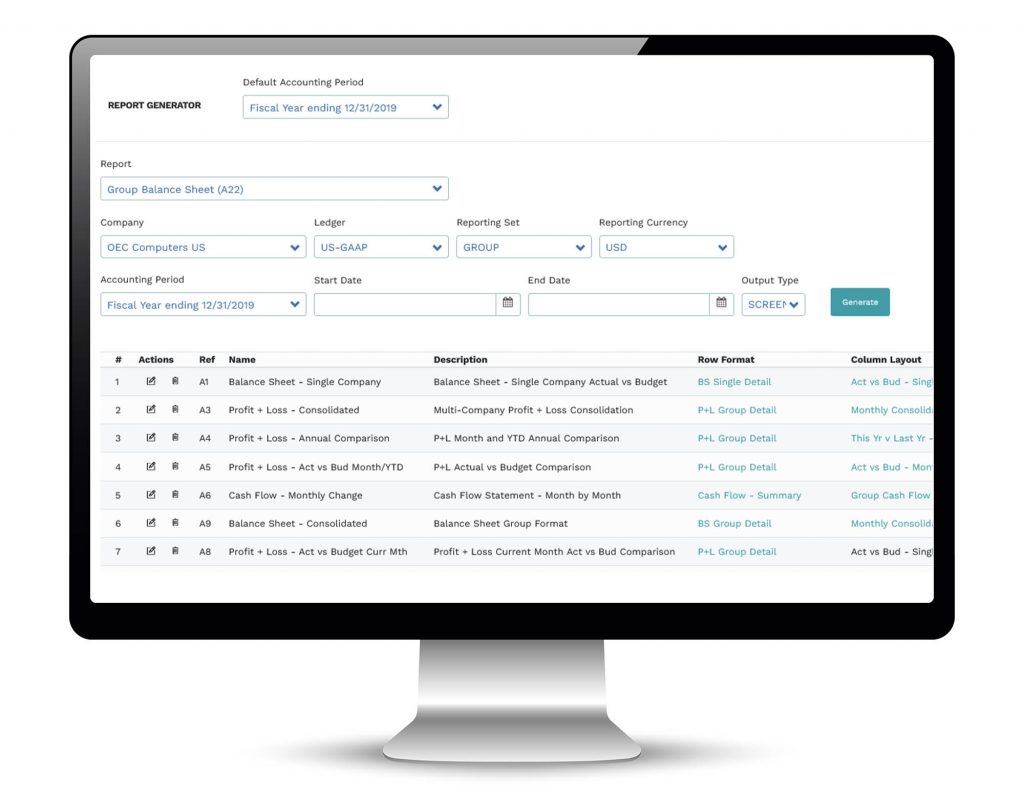
- Mondial’s intuitive report writer supports unlimited and reusable templates with easy-to-manage row formats and column layouts.
- Reports can be presented in multiple output formats including on the screen, via PDF, via email, via web site, downloadable to a spreadsheet, or electronic upload to an external repository.
Issues and Challenges Solved
Key ERP Risks
Mondial Solution
- Lack of standard reporting
- Different ERP Systems
- Lack of Reporting Currencies
- GL Accounts don’t match
- Mismatched Financial Year-End
- Different period lengths
- Incompatible GAAP Approaches
- No access to the details
- No direct access to systems
- Lack of Dimensional Reporting
- Lack of segmented reporting
- Range date reporting is limited
- Lack of Prior Year Comparison
- Limited budget comparison
- Mandatory Reporting Periods
- Statutory Charts of Accounts
- Different GAAP obligations
- Electronic Output Requirements
- Normalizes Data from any ERP
- Multi-ERP Aggregation
- Multi- currency reporting
- Automated Chart Mapping
- Exclude Period-end Adjusts
- Daily Transaction Sorting
- Statutory Charts Adjustments
- Drill down to line level
- All group transactions in the cloud
- Dimensional Value Filtering
- Segment Value filtering
- Daily Accounting Capability
- Year-end transaction filtering
- Unlimited Budget Imports
- Exclude period end adjusts
- Statutory Chart Mapping
- Adjustment Ledgers
- Multi Output Format Standards
How We Help
Financial Reporting
Mondial Financial Reporting Software
Aggregate, normalize, adjust data no matter how disparate they are to ensure accurate and compliant financial reports in any currency, system or language.
Financial Reporting Tools and Professional Services

“Mondial has provided us with financial reporting tools we really needed. We now have a set of reports that can help everyone who uses them better understand the performance of our business. And as we continue to grow Mondial will grow with us. Selecting Mondial really was a great decision.
Matt Scuito
IBP’s Chief Financial Officer
Next Generation Financial Reporting
Discover in-depth articles on Accounting, Finance, Financial Reporting Tools and Digital Transformation. Our expertly curated articles offer a wealth of information and insights to keep you informed and up-to-date.
Listen to thought-provoking discussions on a wide range of Accounting and Finance topics in our podcast section. Our expert guests provide fresh perspectives and insights that challenge and inspire.
Explore our case studies and resources designed to help you better understand how Mondial can greatly help you and your organization.